Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
This article offers a complete guide to diagnosing shoulder aches, masking the anatomy of the shoulder, common reasons for pain consisting of rotator cuff accidents and arthritis, and the numerous diagnostic equipment used, inclusive of bodily exams and imaging strategies. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic method the usage of a shoulder pain diagnosis chart, as it should pick out the supply of aches. Detailed steps for diagnosing precise conditions like frozen shoulder and impingement syndrome are also discussed. The article highlights the blessings of correct prognosis for effective treatment and consists of sensible programs for medical use. Finally, it gives insights into differentiating between similar conditions and information referred to as ache.
Introduction
The shoulder is one of the most complicated joints in the human frame, allowing for a wide variety of movement that is crucial for many daily sports. However, this complexity additionally makes the shoulder vulnerable to various accidents and conditions that could cause giant aches and soreness. Diagnosing the precise purpose of shoulder pain can be hard due to the multitude of viable sources. In this text, we can discover the significance of shoulder health, and commonplace causes of shoulder pain, and provide a comprehensive manual on how to diagnose shoulder pain with the usage of an analysis chart.
Understanding Shoulder Anatomy
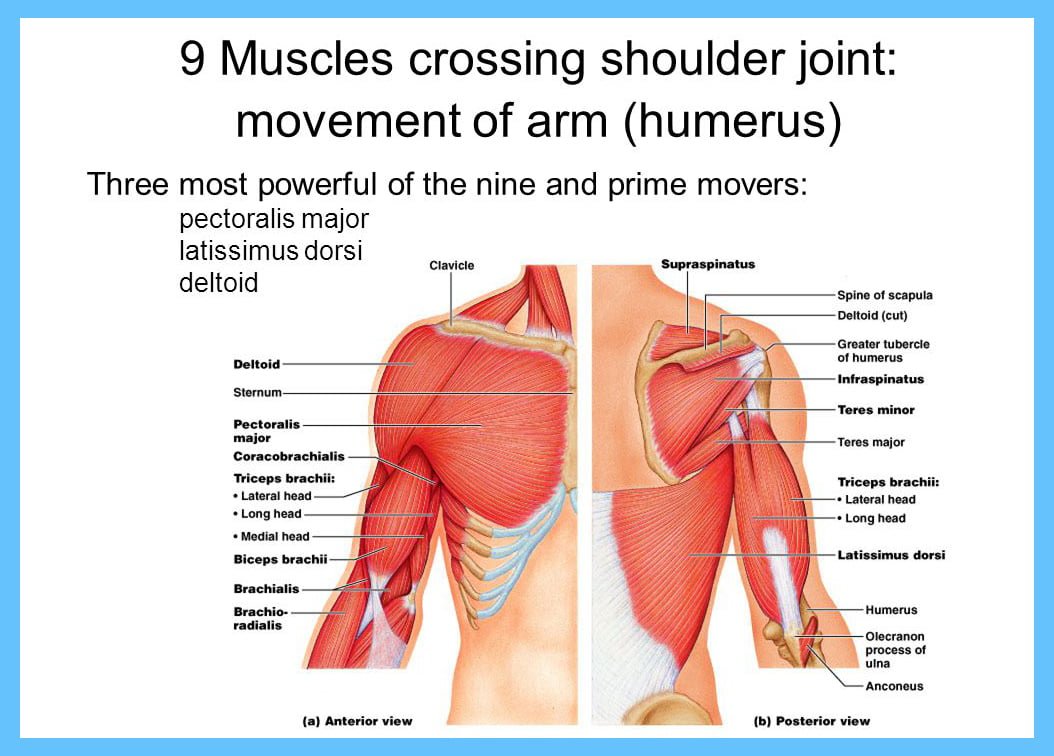
Before diving into the specifics of diagnosing shoulder pain, it is crucial to understand the simple anatomy of the shoulder. The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint, wherein the pinnacle of the humerus (upper arm bone) suits into the glenoid hollow space of the scapula (shoulder blade). This joint is supported via a network of muscle tissues, tendons, ligaments, and nerves, all of which play a role in shoulder characteristics and can be resources for aches.
- Key Components of the Shoulder Joint: The shoulder joint is in general made up of the humerus, scapula, and clavicle (collarbone). The joint’s stability is maintained using the rotator cuff, a group of four muscular tissues, and their associated tendons.
- Muscles Involved in Shoulder Movement: The deltoid, trapezius, and rotator cuff muscle mass are the main muscle mass involved in shoulder movement, allowing movements like lifting, rotating, and achieving.
- Tendons, Ligaments, and Nerves: The shoulder’s tendons join muscle mass to bones, whilst ligaments join bones to bones, imparting balance. Nerves within the shoulder transmit indicators that manipulate movement and sensation.
Common Causes of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain can result from numerous situations, each with awesome traits. Understanding those situations is key to making a correct prognosis.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: These accidents are a few of the maximum commonplace reasons for shoulder pain, specifically in athletes and older adults. They can vary from moderate tendonitis to finish tears of the rotator cuff tendons.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): Characterized by way of stiffness and aches, a frozen shoulder frequently develops gradually and may seriously restrict the range of movement.
- Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: This occurs whilst the rotator cuff tendons are compressed at some stage in shoulder actions, main to pain and irritation.
- Shoulder Arthritis: Arthritis in the shoulder, along with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can cause chronic pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Tendonitis and Bursitis: Inflammation of the shoulder’s tendons or bursae (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joint) can cause giant pain and constrained motion.
- Labral Tears: The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the shoulder socket, and tears in this cartilage can cause aches, instability, and a sensation of the shoulder “catching” in the course of movement.
- Referred Pain from Other Areas: Sometimes, shoulder aches might not originate inside the shoulder itself but can be referred from other regions including the neck, higher again, or maybe internal organs.
Symptoms Associated with Shoulder Pain
Understanding the signs and symptoms associated with shoulder aches can assist narrow down the capacity reasons.
- Pain Characteristics: Shoulder pain can range in depth and best. It can be sharp or dull, localized or radiating to different elements of the arm or back.
- Range of Motion Limitations: A decreased potential to transport the shoulder freely is a commonplace symptom, particularly in conditions like frozen shoulder and rotator cuff accidents.
- Swelling and Inflammation: Visible swelling or a feeling of heat in the shoulder can suggest inflammation, normally seen in arthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis.
- Weakness and Numbness: Weakness in the shoulder or arm, frequently followed with the aid of numbness, can recommend nerve involvement or severe damage like a rotator cuff tear.
Initial Assessment for Shoulder Pain
A thorough preliminary assessment is the first step in diagnosing shoulder aches.
- Patient History and Physical Examination: A specific history can provide clues about the onset, nature, and length of the ache. Questions approximately beyond injuries, pastime stages, and any latest modifications in physical activity are important.
- Pain Location and Its Significance: The unique area of the ache can regularly point to the underlying trouble. For instance, pain on the pinnacle of the shoulder would possibly advise acromioclavicular joint troubles, at the same time as pain at the outer shoulder may indicate rotator cuff problems.
- Identifying the Onset of Pain: Understanding whether or not the pain came on unexpectedly or progressively can assist in differentiating between acute injuries and chronic conditions.
- Impact on Daily Activities: Assessing how shoulder ache impacts everyday existence can offer insight into the severity of the circumstance and manual treatment decisions.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Once the initial evaluation is complete, various diagnostic gear and techniques may be used to affirm the diagnosis.
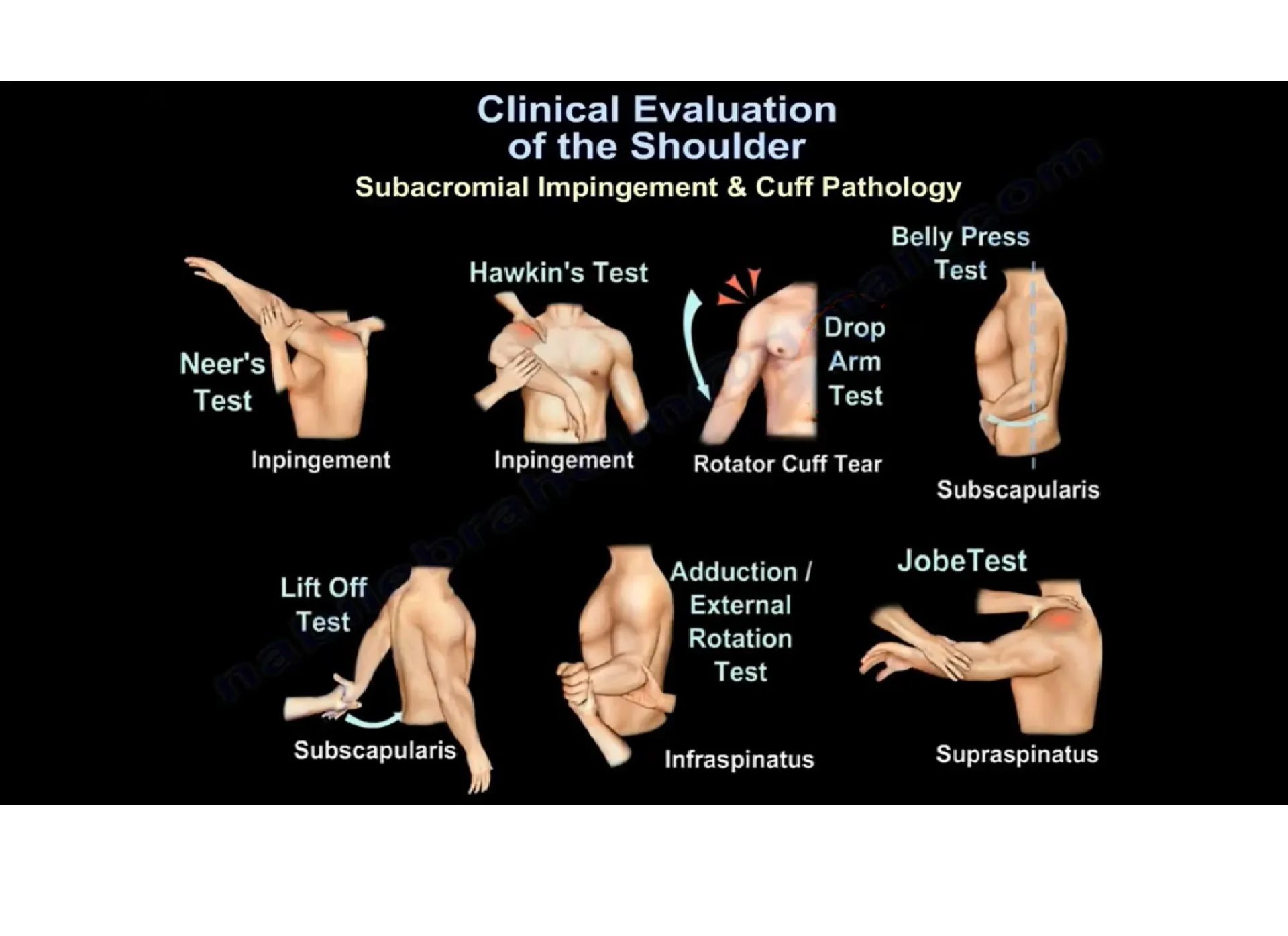
Physical Tests
- Neer’s Test: This check includes lifting the arm whilst preserving the elbow immediately. Pain throughout this motion may indicate shoulder impingement.
- Hawkins-Kennedy Test: This check also tests for impingement by way of having the affected person bend the elbow and rotate the shoulder inward.
Imaging Techniques
- X-rays: Useful for detecting bone abnormalities, fractures, and arthritis.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides exact images of smooth tissues, inclusive of muscle mass, tendons, and ligaments, making it invaluable for diagnosing rotator cuff accidents and labral tears.
- Ultrasound: A value-effective and non-invasive technique to evaluate tender tissue accidents, especially rotator cuff tears.
Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive surgery that allows for direct visualization of the shoulder joint. It may be diagnostic and therapeutic.
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies
These exams determine the electric hobby of muscle groups and the speed of nerve signals, assisting diagnose nerve-associated shoulder pain.
Blood Tests
In instances in which inflammatory or autoimmune situations are suspected, blood exams can discover markers of infection, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and rheumatoid factor.
Creating a Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart
A shoulder pain analysis chart is a crucial device for healthcare providers. It allows systematically compare and file the affected person’s signs and symptoms, physical exam findings, and diagnostic check outcomes.
- Purpose and Importance of a Diagnosis Chart: The chart serves as a visual manual, helping the identity styles that could indicate unique conditions. It helps make certain that every one capability cause is considered and that the analysis isn’t based on assumptions.
- Components of a Diagnosis Chart: Key components include patient records, pain traits, bodily exam findings, imaging effects, and differential diagnoses.
- How to Use the Chart for Effective Diagnosis: The chart is used to move reference signs and check outcomes, making an allowance for a greater accurate and complete prognosis.
Step-by way of-Step Guide to Diagnosing Shoulder Pain
Diagnosing shoulder pain requires a scientific approach. Here’s a step-through-step manual:
- Step 1: Patient History and Symptom Review
- Ask specific questions about the onset, period, and nature of the pain.
- Explore any preceding shoulder accidents or surgeries.
- Step 2: Physical Examination Techniques
- Perform a chain of physical exams, such as the Neer’s and Hawkins-Kennedy assessments, to evaluate a variety of movements and discover unique pain triggers.
- Palpate the shoulder to come across tenderness, swelling, or deformities.
- Step 3: Imaging and Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- Order X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound-based totally on the suspected situation.
- Use arthroscopy if necessary to get an immediate view of the joint.
- Step 4: Interpretation of Results
- Analyze the findings from bodily checks and imaging to narrow down the viable causes.
- Consider differential diagnoses to rule out conditions with comparable signs and symptoms.
- Step 5: Correlating Findings with Potential Causes
- Match the symptoms and take a look at consequences with acknowledged styles of shoulder conditions.
- Use the analysis chart to perceive the most possible cause.
Rotator Cuff Injuries Diagnosis
Rotator cuff injuries are a leading cause of shoulder aches and can range from slight tendonitis to finished tears.
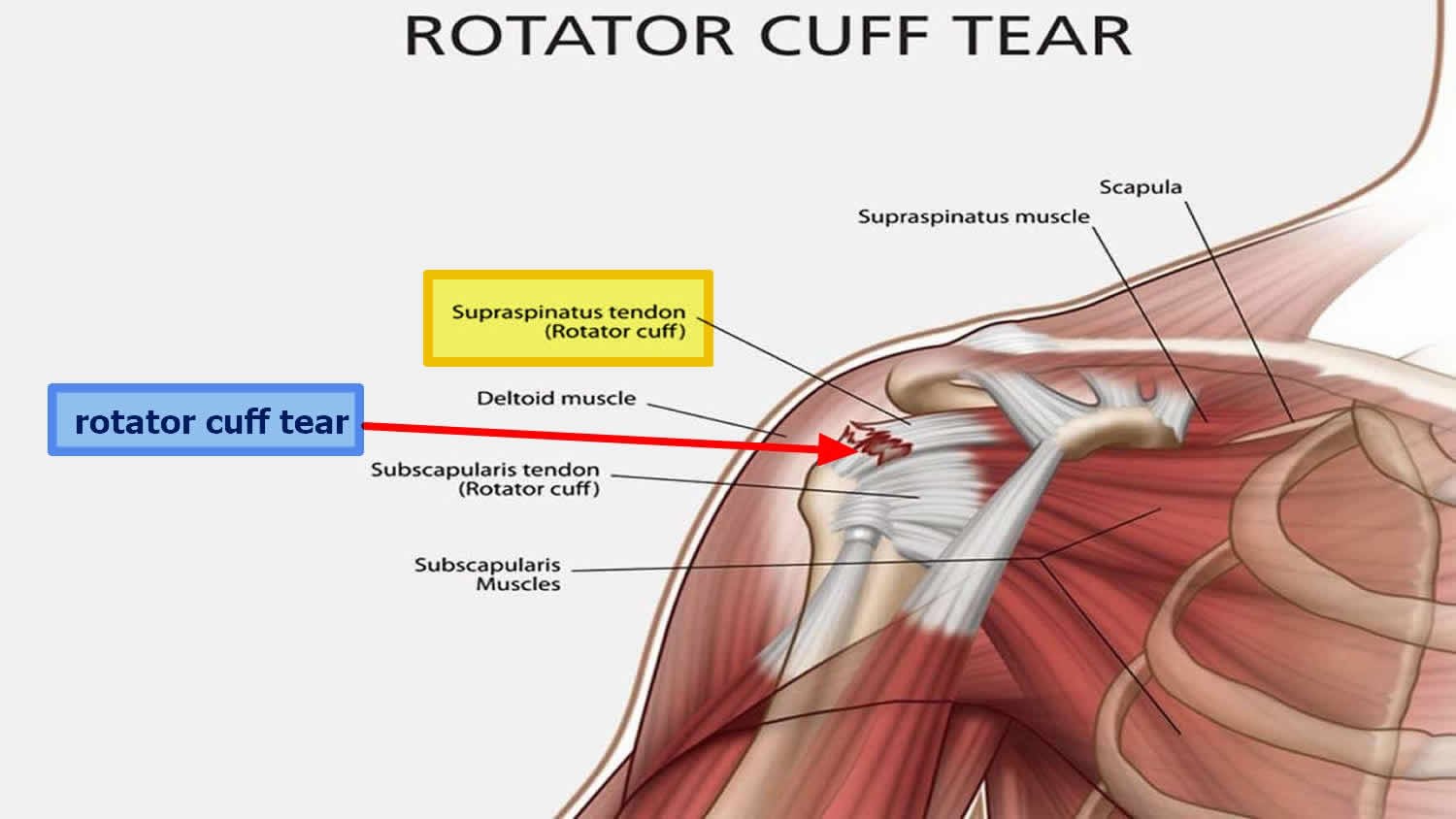
- Specific Symptoms to Identify: Look for ache at the outer shoulder, mainly whilst lifting the arm overhead. Weakness and problems with shoulder rotation are also not unusual.
- Tests and Imaging for Rotator Cuff Tears: Use the Neer’s and Hawkins-Kennedy checks for preliminary evaluation, accompanied by using MRI for an in-depth view of the rotator cuff tendons.
- Treatment Options Based on Diagnosis: Depending on the severity, the remedy may also contain physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, or surgical operations for complete tears.
Frozen Shoulder Diagnosis
Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is characterized by stiffness and a slow loss of movement.
- Key Symptoms and Stages: The circumstance generally progresses through three stages: freezing (ache and stiffness), frozen (stiffness dominates), and thawing (slow development in movement).
- Diagnostic Tests for Adhesive Capsulitis: Diagnosis is in most cases scientific, primarily based on the affected person’s history and bodily examination. Imaging may be used to rule out different causes.
- Differentiating from Other Shoulder Conditions: The hallmark of a frozen shoulder is a significant loss of each lively and passive shoulder motion, differentiating it from conditions like rotator cuff accidents.
Impingement Syndrome Diagnosis
Shoulder impingement takes place while the rotator cuff tendons are compressed during arm actions, leading to pain and irritation.
- Signs and Symptoms of Shoulder Impingement: Patients often feel pain when attaining overhead, and there can be a sense of weak point or a "catching" sensation in the shoulder.
- How to Confirm Diagnosis: Physical tests, consisting of the Neer’s and Hawkins-Kennedy tests, are used to initiate signs. Imaging can rule out other conditions.
- Management and Treatment Strategies: The initial remedy includes rest, anti-inflammatory medicinal drugs, and bodily therapy. Severe instances may also require surgical intervention.
Shoulder Arthritis Diagnosis
Arthritis in the shoulder joint, whether osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, can cause continual pain and stiffness.
- Identifying Arthritis in the Shoulder: Symptoms include deep, aching pain, stiffness, and swelling, especially in the morning or after periods of state of no activity.
- Imaging Techniques for Arthritis: X-rays are the primary device for diagnosing arthritis, showing joint area narrowing, bone spurs, and other degenerative modifications.
- Pain Management and Treatment: Treatment may contain ache comfort medicinal drugs, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, shoulder alternative surgical procedures.
Differentiating Between Tendonitis and Bursitis
Tendonitis and bursitis are not unusual shoulder conditions that may be difficult to distinguish because of overlapping signs.
- Common Symptoms and Overlapping Signs: Both situations reason aches and swelling in the shoulder, frequently worsening with movement.
- Diagnostic Approaches for Tendonitis: Tendonitis is often recognized through a mixture of physical exams and imaging, such as ultrasound or MRI, to assess tendon infection.
- Diagnostic Approaches for Bursitis: Bursitis may be diagnosed via physical exams that provoke ache and imaging that suggests fluid accumulation within the bursa.
- Treatment and Recovery: Both situations are generally treated with relaxation, ice, anti-inflammatory medicines, and physical remedies.
Addressing Referred Pain in Shoulder Diagnosis
Referred pain takes place when the source of the pain is placed in another part of the frame however is felt in the shoulder.
- Understanding Referred Pain: Referred pain is regularly due to conditions inside the neck, chest, or abdomen. For example, coronary heart conditions can cause an ache to be stated in the left shoulder.
- Common Sources of Referred Pain to the Shoulder: Cervical backbone disorders, diaphragmatic inflammation, or even gastrointestinal issues can result in shoulder pain.
- Diagnostic Techniques to Isolate the Pain Source: A thorough examination, which includes a review of systems and potential imaging or different diagnostic exams, is needed to discover the genuine source of the referred ache.
Using the Diagnosis Chart in Clinical Practice
A shoulder pain prognosis chart may be an invaluable device for healthcare companies.
- Case Studies and Practical Applications: Reviewing case studies can assist in understanding how the diagnosis chart may be applied in real-world eventualities. It helps in correlating patient signs and symptoms with particular shoulder conditions.
- Benefits of an Accurate Diagnosis: An accurate prognosis leads to a centered remedy, decreasing the risk of persistent pain and disability.
- Limitations and Challenges of the Diagnosis Chart: While helpful, the analysis chart isn’t always infallible. It must be used as a guide in medical judgment.
Conclusion
Diagnosing shoulder pain as it should be is important for powerful treatment and healing. By knowing the anatomy of the shoulder, recognizing unusual situations, and utilizing a scientific approach with gear like a shoulder ache analysis chart, healthcare companies can drastically improve patient outcomes. The future of shoulder pain diagnosis may also encompass greater superior imaging strategies and personalized treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate take care for their condition.
FAQs about Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart
What are the maximum common causes of shoulder aches?
Rotator cuff injuries, frozen shoulder, shoulder impingement, arthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis are the most unusual causes of shoulder aches.
How is a rotator cuff tear recognized?
A rotator cuff tear is identified through physical exam assessments like Neer’s and Hawkins-Kennedy tests, observed by way of imaging inclusive of MRI for affirmation.
What imaging techniques are best for shoulder aches?
MRI is highly powerful for soft tissue accidents, while X-rays are useful for detecting bone abnormalities and arthritis.
Can a shoulder ache be a signal of a critical circumstance?
Yes, shoulder pain can occasionally suggest severe situations like heart disease or nerve compression. Referred pain has to always be evaluated cautiously.
How can I prevent a shoulder ache from ordinary?
Preventing shoulder pain includes maintaining exact posture, doing regular shoulder-strengthening exercises, and avoiding repetitive overhead activities that stress the shoulder.
My Opinion about Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart
In my opinion, diagnosing shoulder aches requires a cautious and systematic method because of the complexity of the joint and the form of capacity causes. Using a detailed analysis chart, as mentioned in the article, can significantly improve the accuracy of identifying the underlying trouble. This is no longer the most effective results in greater effective remedies however also saves you lengthy-term headaches. Prioritizing thorough checks and embracing advanced diagnostic gear can be key to higher patient consequences.
Disclaimer about Shoulder Pain Diagnosis Chart
The facts provided in this shoulder pain analysis chart article are for instructional functions best and aren’t meant rather for an expert clinical recommendation, analysis, or treatment. Always search for the advice of your physician or other certified fitness issuer with any questions you may have regarding a scientific situation. Do not disregard expert medical recommendations or delay in looking for them because of something you’ve got to examine in this newsletter.